Address
1/3 Harvton st, Stafford, 4053
Hours Of Operation
Monday to Friday: 9AM - 5PM
Address
1/3 Harvton st, Stafford, 4053
Hours Of Operation
Monday to Friday: 9AM - 5PM

In today’s digitalised landscape, cybersecurity has evolved from a niche concern into a crucial national priority. The Australian Government has acknowledged the growing threat of cyber-attacks and other online threats, and on November 22nd published its Cyber Security Strategy 2023-2030.
This comprehensive document, comprised of over 60 pages, outlines the steps the Government will take to reinforce our national cyber resilience. Alongside the strategy, a plan has also been published to detail what initiatives will be taken to enhance Australia’s cyber defences and propel the country as a regional and global cybersecurity leader.
Understanding Australia’s Cybersecurity Strategy
Insights from the Minister for Home Affairs and Cyber Security, Claire O’Neill, act as a basis for this strategy within our evolving technological landscape.

(Source: Facebook)
With innovations like AI, quantum computing, and machine learning reshaping our world, technology has become deeply integrated into all parts of our lives – from connecting with loved ones and helping with carrying out professional duties to entertainment and streaming purposes.
This entwinement with our lives makes everything far more efficient, yet it opens doors to cyber threats like crime, espionage, and misinformation.
The prevalence of cyber-enabled crimes in Australia indicates a growing challenge in cybersecurity. High-profile incidents like the Optus and Medibank data breaches in 2022, affecting millions of customers, underscore this threat. The recent cyber attack on DP World, causing portside delays, further highlights the diverse impact of such crimes.
Furthermore, the 2021-2022 report from the Australian Cyber Security Centre, reported that cyber incidents occurred on average every 7 minutes with over 760,000 cybercrime reports filed.
These events suggest a need for enhanced cybersecurity measures and preparedness by both the government and private entities to protect against and respond to such threats. Australia’s national Cyber Security Strategy, therefore, is a proactive approach towards building our cyber resilience in the evolving, technological transformation period that we are a part of.
The Strategy’s Core Objectives
At its core, the strategy aims to position Australia as a global cybersecurity leader by 2030. This document acknowledges the sophistication and frequency of cyber attacks, emphasising the need for immediate action to protect sensitive data and the community’s most vulnerable members. This includes:

(Source: Cyber Daily)
Legislative Reforms and Initiatives
Ransomware Reporting Obligation
The strategy advocates for a Ransomware Reporting Obligation to provide the Government with better visibility of ransomware threats. This too, designed to be no-fault, no-liability, aims to help facilitate effective management and mitigation of cyber threats and attacks.
Data Retention Requirements
Designed to handle challenges and risks associated with entities that hold large volumes of data for extended periods, this initiative calls to propose amendments to data retention requirements.
Amendments to the Security of Critical Infrastructure Act (SOCI Act)
Proposed changes to the SOCI Act are also suggested, which would enhance the Government’s powers in response to perceived inadequacies. This entails imposing tougher cyber reporting requirements on telecommunication companies and enhancing the cybersecurity obligations of entities involved with critical infrastructure.
Cyber Security Standard for Smart Devices
The Strategy introduces a cyber security standard for Internet of Things (IoT) devices and a voluntary labelling scheme for smart devices. This would be complemented by a code of practice for developers to improve cyber security in software development.
The Three Horizons
The new Cyber Security Strategy will be implemented in three ‘Horizons’.
Horizon 1 (2023-2025) focuses on strengthening Australia’s cyber foundations, addressing all gaps, and building stronger protection for vulnerable communities.
Horizon 2 (2026-2028) will see cybersecurity scaled across the economy, with the Government investing in the cyber ecosystem and cultivating a diverse cyber workforce.
Finally, Horizon 3 (2029-2030) envisions Australia advancing to the forefront of global and regional cybersecurity, leading the way in the development of emerging cyber technologies that can adapt to new risks and opportunities across the cyber landscape.
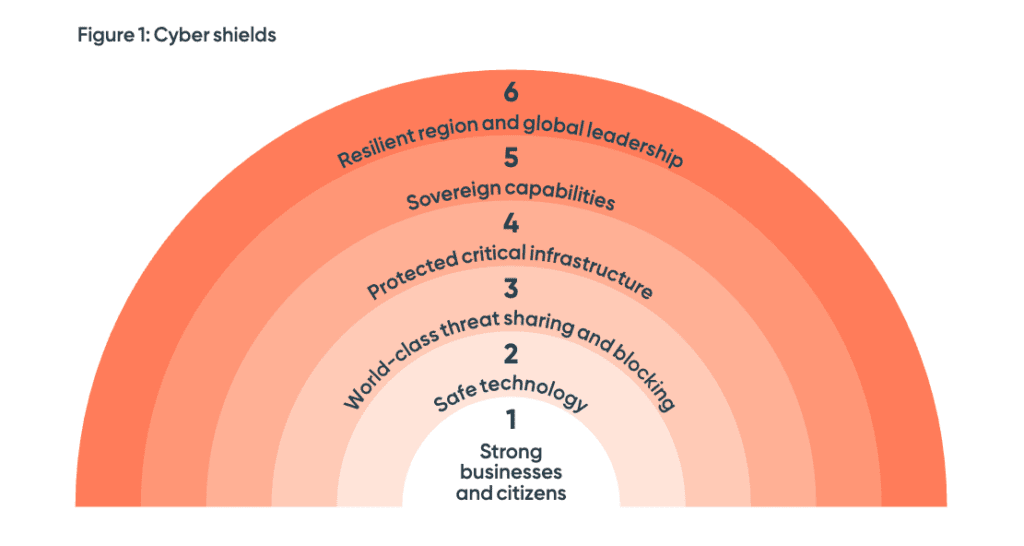
The Six ‘Shields’
Australia’s Cyber Security Strategy for 2023-2030 is centred on the development of six ‘cyber shields’, forming a multi-layered approach to cyber defence. These are:
(Source: 2023-2030 Australian Cyber Security Strategy)
Strong Businesses and Citizens
This shield aims to enhance cyber defences for businesses (particularly small and medium-sized), equipping Australians with the ability to counter cyber threats. Initiatives to support this objective include:
Safe Technology
This focuses on improving the security of technology products and services, especially for vulnerable communities, by enacting legislative actions and standards through:
World-class Threat Sharing and Blocking
This involves developing an extensive threat intelligence network that can alert individuals and businesses. The Government hopes to enhance these capabilities by:
Protected Critical Infrastructure
Through legislative reforms to the SOCI Act, this shield will reinforce security for essential services and infrastructure. Flagged industries include:
Initiatives to be taken under this shield are:
Sovereign Capabilities
This means addressing skill gaps within Australia’s cybersecurity industry and developing and diversifying the cyber workforce to foster a robust sector. Efforts include:
Resilient Regional and Global Leadership
The final shield concentrates on building Australia’s cyber resilience in the APAC region and adhering to international cyber law to foster leadership. This is where:
A Commitment to Cybersecurity
The Cyber Security Strategy 2023-2030 represents Australia’s commitment to a safer, more secure digital future. It balances the rapid digital evolution with robust cybersecurity measures, calling for collaboration among government, industry, and individuals to enhance Australia’s cyber resilience.
In line with this strategy, Red Risk Management recognises the critical role we play in this ecosystem. We are committed to ensuring our services reflect the Government’s initiatives in mitigating cybersecurity risks. Our expertise in risk assessment and management positions us to effectively support these strategic goals, with a particular emphasis on:
We are committed to offering insights and tools that enable our clients to navigate and thrive in this new digital era. Click here to learn more about our services or contact us today to chat with one of our experts.